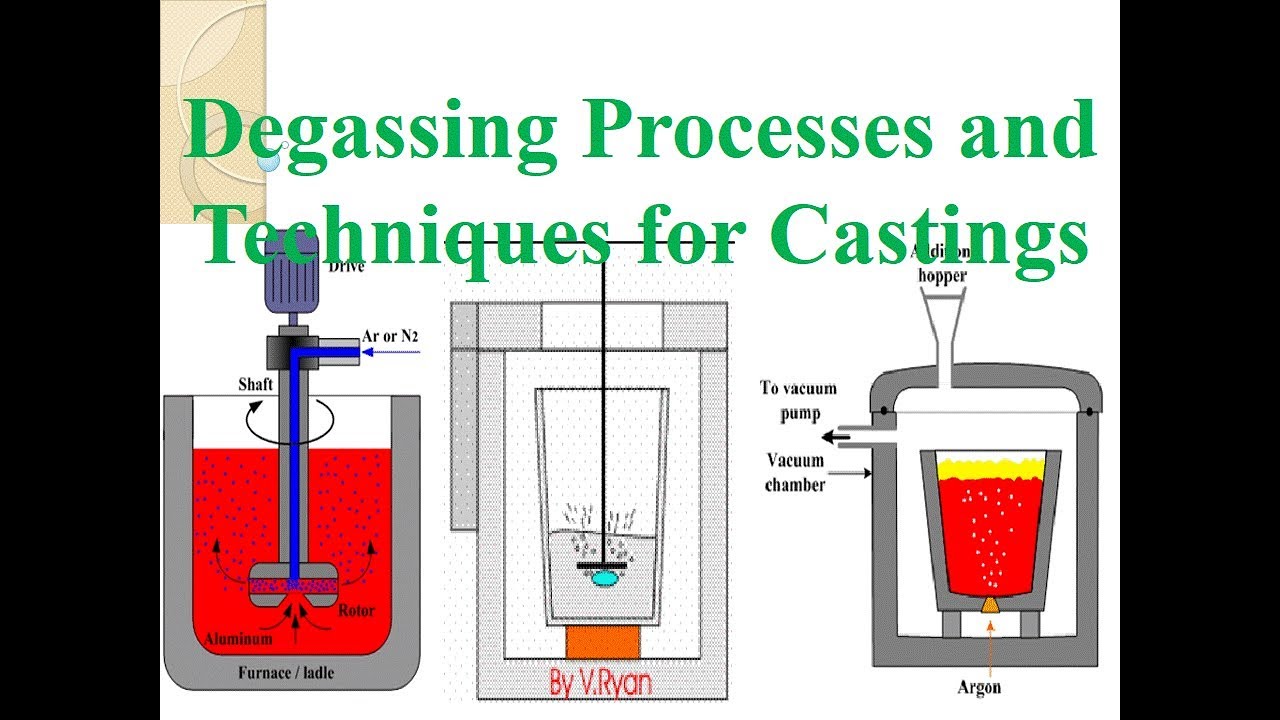
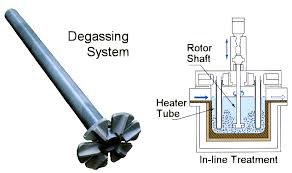
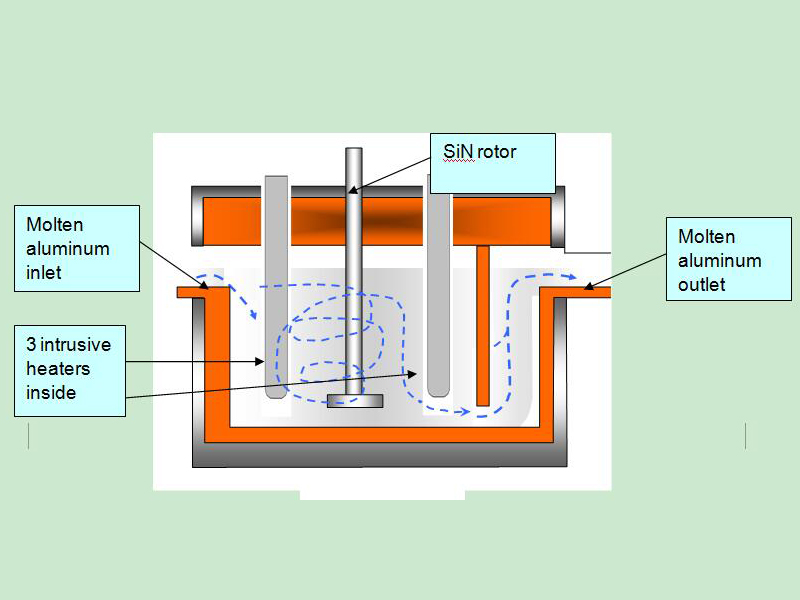
Rotor Online Al Melt Degasser allows nitrogen gas to enter the aluminum melt to generate discrete fine bubbles.
According to the principle of partial pressure, the hydrogen dissolved in the aluminum melt is under the effect of the pressure difference.
Continue to diffuse into the bubble. When the bubble rises to the liquid level, the hydrogen diffused into the bubble enters the atmosphere together with the bubble.
At the same time, the bubble surface can automatically adsorb inclusions, and the inclusions float to the liquid surface to form slag.

As the first process of aluminum processing, if the aluminum billet has inherent defects caused by melting (such as inclusions, etc.), no matter what advanced technology or equipment is used, it cannot be used in a series of subsequent processing processes (such as Rolling, extrusion, heat treatment, surface treatment, etc.) to make up for this congenital defect, and then it is difficult to ensure the quality and performance of aluminum products.
Therefore, in order to give full play to the potential of the material and give full play to its own performance, the production and quality control problems of the cast slab must first be solved.
The main source of hydrogen in aluminum alloy melt is that in the process of aluminum alloy melt, moisture in the atmosphere and on the surface of raw materials enters the alloy melt through metallurgical reactions, which causes the melt to absorb hydrogen.
There are two forms of its presence in molten aluminum.
About 90% of the hydrogen is dissolved in the melt as interstitial atoms.
About 10% of a small amount of hydrogen is adsorbed on the surface or gap of inclusions in the form of bubbles, forming hydrogen bubbles with a negative radius of curvature.
The main function of Rotor Online Al Melt Degasser is to remove H from the aluminum melt to ensure the quality of the aluminum melt.
The presence of hydrogen will adversely affect the performance of aluminum alloys.
The hydrogen in aluminum and its alloys can create pores of various sizes in the billet, destroy the continuity of the metal material, and reduce the effective cross-section of the part.
The stress concentration around the hole will greatly reduce the processing performance of the cast slab.
In semi-finished products, there will be delamination defects caused by hydrogen and the second type of hydrogen embrittlement, which will increase the brittleness of the alloy during forging and rolling.
The supersaturated and combined state of hydrogen is an important reason for the secondary porosity and surface blistering of the cast slab during the homogenization process.
Ceramic foam filters are basically divided into 6 pore sizes: 10PPI, 15PPI, 20PPI, 25PPI, 30PPI, and 40PPI. The larger the number, the smaller the aperture. But in actual practice, the four types of 10PPI 20PPI 30PP 40PPI can meet the needs of customers.
Aperture selection
1. The casting: 10~25ppi
2. Semi-continuous casting: 30~60ppi
3. High-quality aluminum or sheet: 50~60ppi
4. Continuous casting and rolling: 50~60p